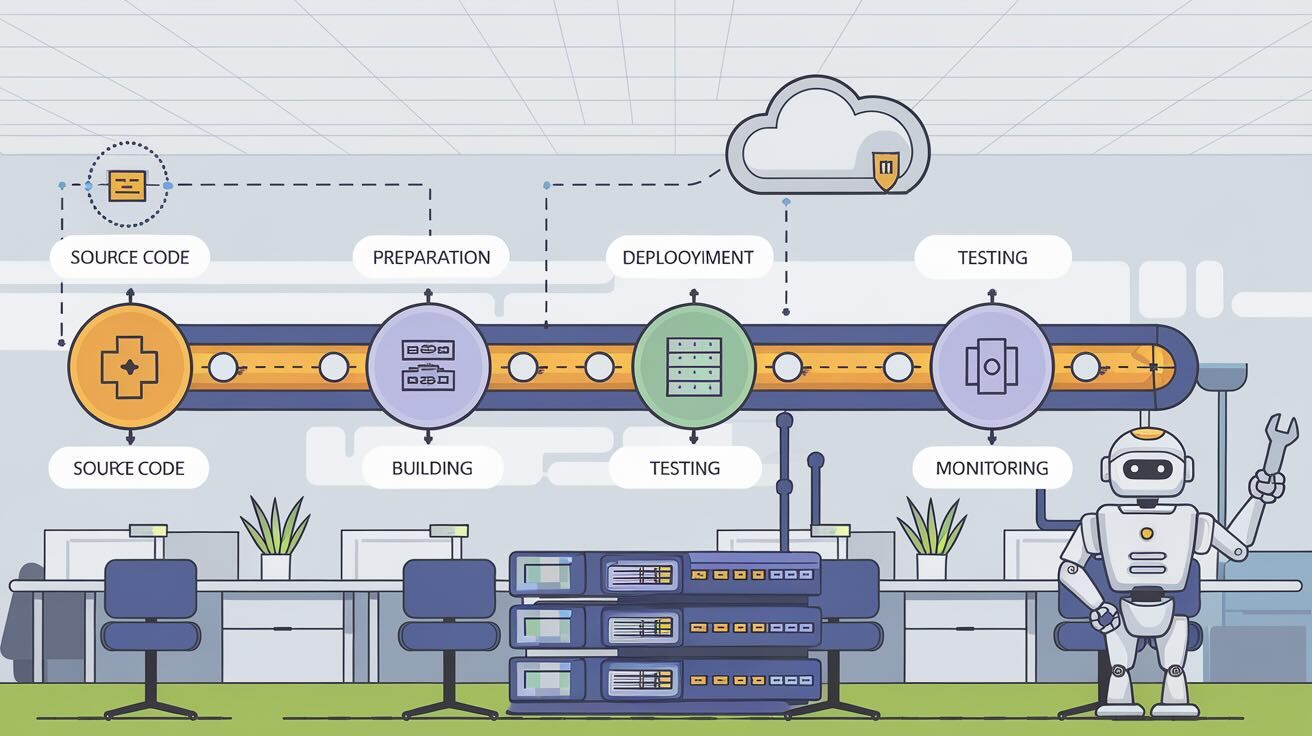
A build pipeline is a structured, automated workflow that converts source code into a production-ready artifact. The build pipeline process ensures that code is compiled, tested, and deployed without manual intervention, making it a critical component of DevOps automation.
Why Are Build Pipelines Important in DevOps?
- Automation: Automates repetitive tasks, reducing human error and saving time.
- Quality Assurance: Enforces code quality standards through automated testing.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Streamlines the deployment process, allowing for quicker releases.
- Consistency: Ensures consistent builds and deployments across different environments.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration between development and operations teams.
A build pipeline process typically follows these key stages:
- Source Code Check-in: Developers commit their code changes to a version control system like Git.
- Build Stage: The source code is compiled into a deployable artifact (e.g., JAR, WA, WAR, or Docker image.
- Testing & Validation: Automated tests verify code quality, functionality, and security. Includes unit tests, integration tests, and static code analysis.
- Artifact Storage: Successful builds are stored in a build repository (e.g., JFrog Artifactory, Nexus).
- Deployment to Environments: The built artifact is automatically deployed to staging, UAT, or production environments.
- Monitoring & Logging: Post-deployment monitoring ensures performance, stability, and rollback strategies.
Benefits of Using a Build Pipeline Tool
A robust build pipeline tool can significantly enhance your development workflow. Here are some key benefits:
- Centralized Management: Manage and monitor your entire pipeline from a single interface.
- Parallel Processing: Speed up the build process by running tasks concurrently.
- Customizable Workflows: Tailor your pipeline to fit your specific project needs.
- Integration with Other Tools: Seamlessly integrate with version control systems, testing frameworks, and deployment tools.
- Detailed Reporting and Analytics: Gain valuable insights into your pipeline performance.
Build Pipeline vs. Build Server: A Key Difference
While both terms are related to the software development process, they represent distinct concepts:
Build Server:
- Physical or Virtual Machine: A dedicated machine or virtual environment used to execute build processes.
- Execution Environment: Provides the necessary tools, compilers, and libraries to compile, test, and package code.
- Task Runner: Often employs tools like Jenkins, TeamCity, or Atlassian Bamboo to orchestrate the build process.
Build Pipeline:
- Sequence of Steps: A series of automated steps that transform source code into a deployable artifact.
- Workflow: Defines the order of tasks, such as compiling, testing, and packaging.
- Integration with Tools: Leverages build servers and other tools to execute the pipeline stages.
Key Difference:
A build server is a tool used within a build pipeline. The pipeline defines the process and the server provides the environment to execute that process. In essence, a build pipeline is a concept, while a build server is a physical or virtual implementation.
DeployHQ is a powerful tool that helps automate build pipelines, streamlining continuous integration (CI) and deployment (CD) workflows for faster, error-free releases. By automating tasks and ensuring consistency, you can accelerate your software delivery and reduce the risk of errors.
FAQs
What is a build pipeline process?
A build pipeline process consists of automated steps that compile, test, and deploy software, ensuring fast and reliable code releases.
How does a build pipeline work in DevOps? A build pipeline in DevOps automates the process of transforming source code into a deployable application, integrating with CI/CD workflows.
What are the best tools for building a pipeline? Popular build pipeline tools include Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, and DeployHQ for automating deployment workflows.
This post is part of our "What Is" series, helping developers understand key concepts and methodologies in modern software development.